CNC prototype make precise 3D models via CNC machining for rapid prototyping. In this article, we’ll walk you through CNC prototyping, and our team will bring your designs to life with unparalleled quality and efficiency.
General CNC Machining & CNC Prototype Machining
CNC machining manufacturing utilizes computer-controlled automated equipment or systems to handle and process materials to create parts or products. CNC prototyping takes CAD files and feeds them into a CNC machine for prototyping and manufacturing.
Specifically, the main goal of Обработка на станках с ЧПУ manufacturing is the mass production of highly accurate and repeatable parts or products. It is commonly used in industrial production. CNC prototyping, on the other hand, focuses on smaller-scale, individualized needs. For example, to quickly produce a single or a small number of prototype samples for functional testing or user feedback. It is often used in design and development, research and experimentation.
In addition, CNC prototyping usually requires higher precision and wider adaptability. This is because it needs to meet the manufacturing and testing requirements for high-quality prototypes, including shape, size, and surface quality. Comparatively, CNC machining manufacturing can have relatively lower requirements, as it is primarily concerned with efficient and cost-effective manufacturing.
In conclusion, CNC machining manufacturing and CNC prototyping are both very important technologies in the modern manufacturing field, and they have a close connection and interaction, but there are also some differences.
CNC Prototype Machining Service
Manufacturing Process
CNC Engraving:
Engraving and cutting on the surface of a material using a cutting tool. Suitable for producing flat or curved surface prototypes.
CNC Milling:
Removing excess material from the surface of a material by rotating a tool. Suitable for prototyping complex shapes and structures.
CNC Dispensing:
Utilizes robots or automated dispensing equipment to control the flow rate and position of the glue to be dispensed onto the material. Suitable for making prototype parts that need to be glued.
CNC Mold Making:
The process of making injection molds, die casting molds, and other types of metal molds. Used for high volume production of prototypes that require plastic or metal molding.
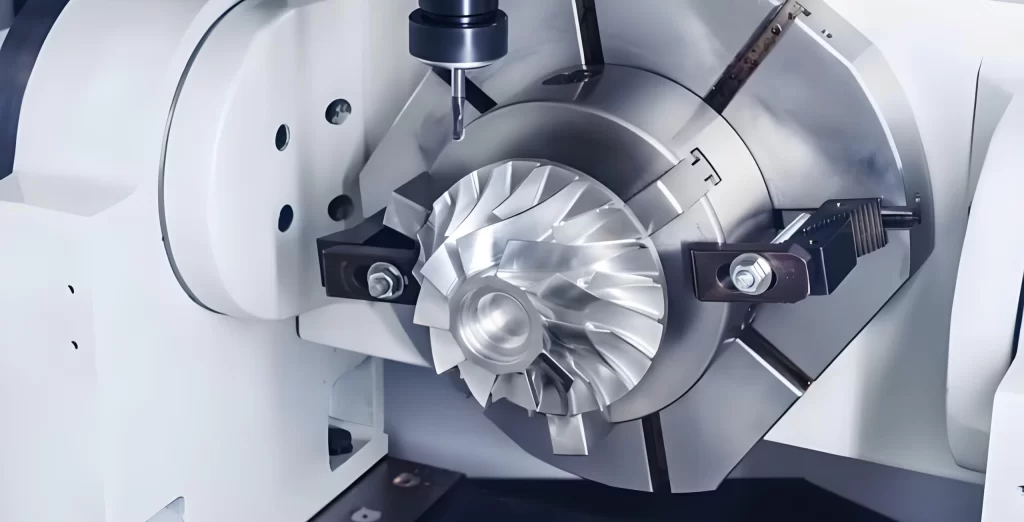
Main Stages
Design:
In the design phase, the initial design of the product needs to be accomplished by hand drawing, CAD design software, or other aids. This phase focuses on determining the size, form and function requirements of the product.
Manufacturing:
In the manufacturing phase, the product is machined and molded from the design drawings or 3D models. This phase focuses on selecting the right materials and manufacturing methods, such as CNC machining, 3D printing, laser cutting, etc., and ensuring that the manufactured prototype meets the design requirements.
Testing:
In the testing phase, the manufactured prototype needs to be inspected and tested to ensure that it meets the design requirements and functional requirements. The focus of this phase is to test various indexes, such as strength, wear resistance, service life and so on.
Correction and Improvement:
After problems are found during testing, the prototype needs to be corrected and improved to achieve better results. This phase focuses on understanding the test results and making adjustments and improvements based on experimental data to improve the quality and performance of the prototype.
Материалы
Металлы
Metal raw materials are characterized by high strength, high toughness, resistance to wear and good thermal conductivity. Commonly used in the manufacture of parts that need to withstand high pressure or operate in high-temperature environments.
Aluminum Alloy:
Aluminum alloy has the characteristics of light weight, high strength, good workability, etc. It is widely used for prototype manufacturing in aerospace, automotive, electronics and other fields.
Steel:
Steel is characteristically strong, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant. It is a good choice for manufacturing parts that need to withstand high pressure or work in high-temperature environments, such as mechanical equipment and automobile parts.
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel has good corrosion resistance, high surface finish, easy to maintain and other characteristics, commonly used in the manufacture of high-end products, such as shells, accessories.
Copper:
Copper has good electrical conductivity, good thermal conductivity, good processability and other characteristics, commonly used in electronics, building decoration, artwork and other areas of prototype manufacturing.
Magnesium Alloy:
Magnesium alloy has lightweight, high strength, good seismic performance and other characteristics, commonly used in the manufacture of cell phone parts, automotive seat skeleton and so on.
Zinc Alloy:
Zinc alloy has a low melting point, good plasticity and other characteristics, commonly used in the manufacture of precision mechanical parts, electronic devices shell.
Titanium Alloy:
Titanium alloy has high strength, low density, corrosion resistance and other characteristics, widely used in aviation, aerospace, medical and other fields of prototype manufacturing.
In addition to the above materials, there are many other metal materials to choose from, such as nickel alloys, ferroalloys, cast iron and so on. When choosing metal prototyping materials, you need to select the most suitable material for yourself and your project according to the actual needs and requirements.
Пластик
Plastic is one of the most common prototype materials. Its low cost, easy processing, free color mixing and painting make it widely used in various industries.
ABS:
ABS is a commonly available engineering plastic with good processability and mechanical properties. It is commonly to make electronic product shells, home appliance parts, models and so on.
PC:
PC is a high-strength, high-toughness plastic material with good heat resistance and UV resistance.
POM:
POM is a high-strength, rigid plastic material with good abrasion and chemical resistance, usually for making mechanical parts, bearings, pulleys and so on.
PMMA:
PMMA is a transparent plastic material with good optical properties and weather resistance, and is commonly in use for lampshades, display racks and decorative items.
PA:
PA is a high-strength, high-toughness engineering plastic with good mechanical and wear properties. Due to its light weight, corrosion resistance and other characteristics, PA is often used in automotive, aviation, electronics and other fields.
PP:
PP is a lightweight, high-strength, corrosion-resistant plastic material with good plasticity and mechanical properties. It is commonly applied in the manufacture of automobile parts, containers and home appliance parts.
In addition to these materials, there are many other plastic materials that can be use in the CNC prototyping, such as PTFE, PVC and EVA. When selecting a material, you need to consider the requirements of the prototype and the application scenario and choose the most suitable material.
Advangates of CNC Prototype
CNC machining allows for very high machining accuracy and repeatability, reducing errors and waste, thus improving the quality of prototypes.
CNC machining can automate the machining process, greatly reducing the production cycle and thus increasing the speed and efficiency of prototyping.
CNC machining can machine a wide range of different materials, including plastics, metals, wood, etc., and allows for quick changeover to different tools and fixtures to accommodate prototypes of all shapes and sizes.
Programming through the digital control system allows for completely consistent machining results, thus ensuring repeatability of prototypes.
CNC machining allows toolpaths and operating parameters to be adjusted as needed, making it easy to modify and improve prototypes.
CNC machining saves costs by reducing labor, time and material consumption compared to traditional manual production.

Limitations of CNC Prototype
Material Limitations:
CNC machining requires the selection of materials that are suitable for machining and cannot handle materials that are too hard, too brittle or too soft.
Large Size Limitations:
CNC machining equipment has a limited range and cannot handle prototypes that are too large.
Overly Complex Geometries:
For prototypes with very complex, detailed, and tortuous geometries, CNC machining can require extremely complex toolpaths and machining programs to achieve, making it more difficult and costly to produce.
High Software Programming Requirements:
CNC machining requires the use of specialized CAD/CAM software for programming, which requires a certain level of skill and experience, as well as the skills and knowledge of the designer.
Environmental Concerns:
CNC machining consumes a lot of energy and materials, and the waste and wastewater generated during the machining process need to be properly treating in order to meet the environmental requirements.
Applications of CNC Prototype
Автомобиль:
Used for automotive parts prototyping, automotive mold manufacturing, etc.
Аэрокосмическая промышленность:
Used for aircraft parts, aircraft engine parts, spacecraft prototyping, etc.
Medical Device:
For medical device prototyping and medical device mold manufacturing.
Industrial Design:
Used for prototyping various products, such as cell phones, computers, home appliances and other products.
Education and Training:
Used for teaching and experimentation in schools and training institutions to help students better understand and master CNC machining technology.
Creators & Personal Prototyping:
Used for creators and individuals to make all kinds of small batch or single prototypes to realize the demand of personalized customization.

CNC Machining Prototypes & Injection Molding Prototypes
CNC machining manufacturing is a manufacturing process. It utilizes computer-controlled automated equipment or systems to handle and process materials to create parts or products.CNC prototyping is a branch of CNC machining manufacturing. It involves inputting CAD files into a CNC machine for prototype machining and manufacturing.
Specifically, the main goal of Обработка на станках с ЧПУ manufacturing is the mass production of highly accurate and repeatable parts or products. It is commonly used in industrial production. CNC prototyping, on the other hand, focuses on smaller-scale, individualized needs. For example, to quickly produce a single or a small number of prototype samples for functional testing or user feedback. It is often used in design and development, research and experimentation.
In addition, CNC prototyping usually requires higher precision and wider adaptability. This is because it needs to meet the manufacturing and testing requirements for high-quality prototypes, including shape, size, and surface quality. Comparatively, CNC machining manufacturing can have relatively lower requirements, as it is primarily concerned with efficient and cost-effective manufacturing.
In conclusion, CNC machining manufacturing and CNC prototyping are both very important technologies in the modern manufacturing field, and they have a close connection and interaction, but there are also some differences.







