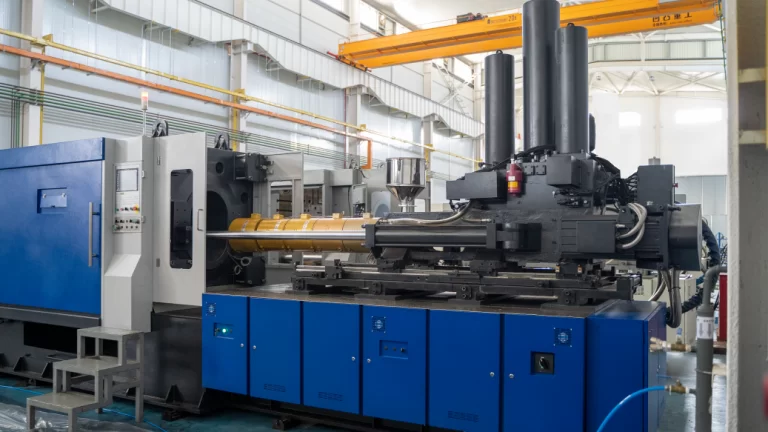
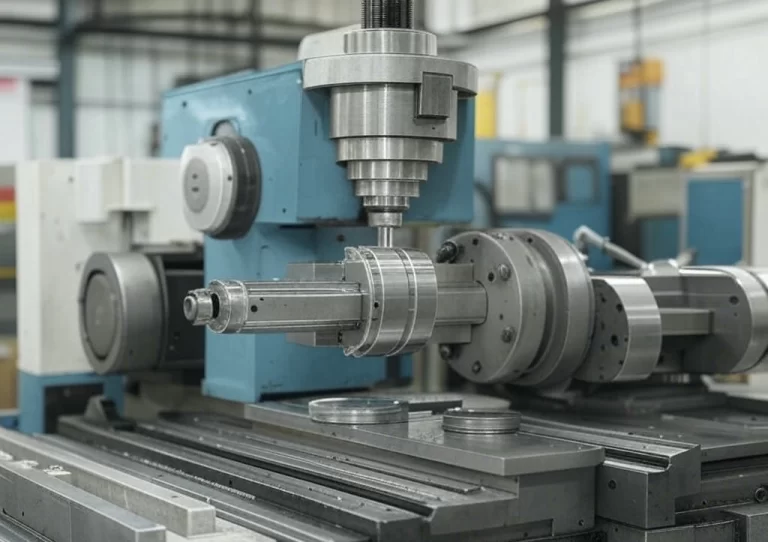
CNC Turned Parts are parts manufactured through CNC turning processing technology. It is a high-precision, high-efficiency machining process that utilizes computer control. It mainly manufactures parts with complex geometries, such as cylinders, cones and threads.
Machining Principle of CNC Turned Parts
CNC lathe controls the movement trajectory of the tool through the computer program to cut and process the rotating workpiece. The specific process is as follows:
Workpiece Clamping: The workpiece is fixed on the spindle and rotates with the spindle.
Tool Movement: The tool moves along the X-axis (radial) and Z-axis (axial) according to the program instructions to cut.
Cutting Process: The tool contacts the workpiece to remove excess material and form the desired shape and size.
Automatic Tool Change: Some CNC lathes are capable of automatically changing different tools according to the program. So this enables it to complete multiple processes.
Cooling And Chip Removal: Coolant is used to reduce temperature during machining, and chips are removed by chip removal system.
The core of CNC lathe lies in its control system. It can accurately control the tool trajectory, speed and other parameters to ensure machining accuracy and surface quality.

Types
Shaft CNC Turned Parts
Drive shafts, spindles, screws and so on.
Large length and diameter, usually require high precision and high surface quality.
Disk CNC Turned Parts
Flanges, end caps, gear blanks, etc..
Large diameter, small thickness, often used for connection or sealing.
Sleeve CNC Turned Parts
Bearing bushings, bushings, hydraulic cylinder bushings and so on.
High internal and external coaxial requirements, often used for support or positioning.
Complex Surface Parts
Turbine blades, molds, cams and so on.
Complex shape, usually requires multi-axis machining.
Threaded CNC Turned Parts
Bolts, nuts, threaded shafts, etc.
Threads require high precision and are often used for connection or transmission.
Shaped CNC Turned Parts
Eccentric shafts, non-circular cross-section parts, etc.
Lrregular shape, difficult to process.
Application Areas
Aerospace
Used in the manufacture of engine parts (such as turbine shafts, blades), fuselage structural parts, etc..
Requirements for lightweight materials, high temperature resistance, high strength.
Automotive Manufacturing
Used in the manufacture of engine parts (such as crankshafts, camshafts), transmission system parts (such as gears, shafts), etc.
Requirements for high precision, high wear resistance.
Machinery Manufacturing
Used in the manufacture of bearings, gears, shaft parts, hydraulic components, etc.
High rigidity and durability are required.
Electrical And Electronic
Used for manufacturing precision parts (such as connectors, heat sinks), etc.
High precision and surface finish are required.
Medical Devices
Used in the manufacture of surgical instruments, implants (such as artificial joints), etc..
Biocompatibility and high precision are required.
Energy Industry
Used in the manufacture of nuclear power, wind power equipment in the key parts.
Requirements for high reliability and corrosion resistance.

Machining Process
Process Design
Determine the machining process route according to the parts drawing.
Selection of suitable tools, fixtures and cutting parameters.
Roughing
Rapid removal of excess material, close to the final shape.
Mainly focus on machining efficiency.
Semi-finishing Machining
Further improve the dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
A small allowance is made for finishing.
Finishing
Achieve the dimensional accuracy and surface roughness required by the drawing.
Use high-precision tools and low-speed cutting.
Heat Treatment
Harden and temper the parts to improve the material properties.
Surface Treatment
Such as chrome plating, spraying, polishing, etc., to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
Testing And Inspection
Use coordinate measuring machine, profiler and other equipment to test the size and shape accuracy.

CNC Turning Machining Equipment
Ordinary CNC Lathe
Two-axis control (X-axis and Z-axis), suitable for simple shafts, disk parts processing.
Turning Center
Integrated turning and milling functions, equipped with power tools and C-axis, suitable for complex parts processing.
Multi-axis CNC Lathe
Such as four-axis, five-axis CNC lathe, can realize multi-axis linkage, suitable for complex surface parts processing.
Vertical CNC Lathe
Vertical spindle arrangement, suitable for processing large disk parts.
Horizontal CNC Lathe
Spindle arranged horizontally, suitable for processing long shaft parts.
Automated Production Line
Integration of multiple CNC lathes, robots, conveyor systems, to achieve automated production.

Advantages
High Precision
CNC system is capable of realizing micron-level precision.
High Efficiency
Automated machining reduces manual intervention and improves productivity.
Flexibility
Different parts can be processed by modifying the program.
Complex Shape Processing
Multi-axis linkage can process complex surfaces.
High Consistency
Excellent part consistency in mass production.